


Next: Suggestions for labs
Up: Lecture plans
Previous: Topic: Introduction to
The problem
Convert English text into the vowel and consonant sounds (phonemes)
that make up speech. For example consider the following words:
misled, hors d'oeuvres, and bedraggled.
Traditional Approach
- Create if-then rules to encode all the regularities in the
language.
- Maintain a database of exceptions to these rules.
- Build a production system to resolve conflicts.
For example, a ``c'' can either be pronounced like an ``s'' as in
center, icy, and city or a ``k'' as in cat and crumb. Here is a rule
that might encode this difference:
if a ``c'' appears before an ``i'', ``e'', or ``y''
then pronounce it like an ``s''
else pronounce it like a ``k''
Exception: celtic
Network Approach
Allow a system to learn how to pronounce words by giving it lots of
examples and correcting its mistakes.
- Choose an architecture.
- Choose a representation for the input and output.
- Determine a training set. 16,000 words were chosen randomly from
the 20,000 words in Webster's Dictionary.
- Train the system. Give the network each word in the training set
several times, and indicate the errors for learning.
- Test the system. The network was able to respond correctly to
90%of the 4,000 remaining words from the dictionary.


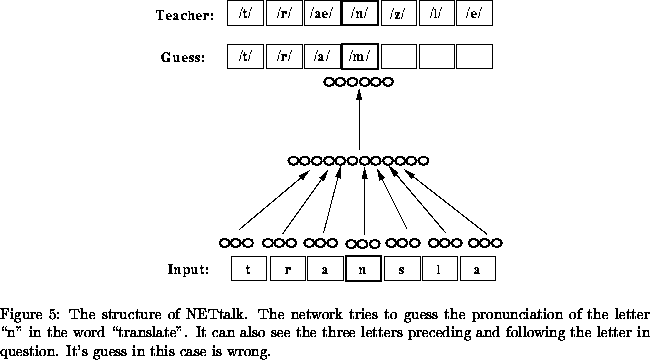
Advantages of the Network Approach
- There may exist non-intuitive relationships between the problem's
parameters that are easy for the network learning procedure to take
advantage of but hard for a programmer to recognize
- A network can consider a much larger number of inputs and
outputs (ranging in the thousands) than is computationally feasible
for most traditional methods
- A network solution may often require less hardware and less
software leading to lower costs and faster design cycles
Transcript from the NETtalk audio tape
- Babbling
- Consonant and vowel sounds
- Pauses
- Words
- Phrases
- Full sentences
... when we walk home from school. I walk with two friends and
sometimes we can't run home from school now. Because ?? every time
she wants to run. She gets very ?? and stuff. And then she can't
breathe very well and she gets sick. That's why we can't run. I like
to go to my grandmother's house because she gives us candy. Well and
we eat there sometimes. Sometimes we sleep over night there.



Next: Suggestions for labs
Up: Lecture plans
Previous: Topic: Introduction to






